How to pick the right Diamond

Courtesy of yalibnan.com As they say ' diamonds are forever'. If this is the case you might as well learn how to pick your diamond in order to enjoy it forever. In this article we will explain the step by step approach to buying diamonds, in order to allow the shopper to compare in a logical manner one diamond to another. There are internationally recognized specifications that all Diamond traders use. These specifications are called 5C's. The 5 C's are: Carat - Color - Clarity - Cut - Cost
Carat :
This defines the weight of the diamond
The larger the carat the higher the price
One carat is equal to 0.20 gram
It is very important not to mistake carat weight with the dimension of a diamond. Because different cuts of diamonds will have different dimensions , even if they were the same carat weight.
Prices of diamonds are expressed in the trade as a price per carat. So when we say that the Carat Weight has the biggest impact on the price of the stone, we refer to the unit price per carat, not just the overall price of the whole stone.
Example 1: These are examples only and do not reflect the actual price.
Diamond "A" = 0.25 carats and costs $1,000 per carat. $1,000 x 0.25 = $250/stone.
Diamond "B" = 0.50 carats and costs $1,250 per carat. $1,250 x 0.50 = $625/stone
How "big" is a carat?
Since it is not easy to weigh a diamond, specially if it is already mounted. The best way to find out its carat weight is to measure its diameter. The table below gives you an approximate size in mm based on the carat weight
0.25 ct. - 4.1 mm 0.50 ct. - 5.2 mm
0.75 ct. - 5.9 mm 1.00 ct. - 6.5 mm
How much does "carat weight" affect cost?
Let's take a typical Diamond for an example, and see what happens when we take it through different carat weights.
A Diamond of G color and SI1 Clarity will be in one Category of prices when it is between 0.50 - 0.69 carats. When you take that same quality Diamond and increase the size to the next price category, which is the 0.70 - 0.89 carat range, the price increase will be approximately $1,100 per carat. Increase to the 0.90 - 0.99 carat range, and the price increase will be approximately another $800 per carat. Increase to 1.00 - 1.49 carat range, and the increase will be approximately another $800 per carat. If you increase to the 1.50 - 1.99 carat range, the price increase will be approximately $1,200 per carat.
In other words a diamond that is 1.0 carat is approx equals to : 1250+1100+800+800
=3950 /carat
While the .5 carat diamond of same color and clarity will be 1250x.5= 625
2 diamonds of 0.5 carat each = 1 carat = 1250
In other words the price of 1 carat diamond is much higher than 2 diamonds of 0.5 carat each. In this example it is 3950/1250 = 3.16 times higher.
Color
The color of a diamond has the second biggest impact on its price, after carat weight. Did you know that diamonds come in every color of the rainbow?
Grading color in the normal range involves deciding how closely a stone's body color approaches colorlessness. Most diamonds have at least a trace of yellow or brown body color. With the exception of some natural fancy colors, such as blue, pink, purple, or red, the colorless grade is the most valuable.

If a diamond does not have enough color to be called fancy, then it is graded in a scale of colors ranging from Colorless to Light Yellow, "D" through "Z". A diamond with a "D" color is considered to be colorless. If the color is more intense than "Z", it is considered fancy. A fancy yellow diamond fetches a higher price than a light yellow diamond.
The Laboratories only grade diamonds which are unmounted , or "loose", and they do so under special light. Once a loose diamond is mounted on a ring, even the trained professional cannot always tell the difference between, say a "D" color and an "E" or "F" color diamond!
How much does "color" affect cost?
Let's take a typical Diamond for an example, and see what happens when we take it through different color grades.
Let's start with a 1.00 carat Diamond of K color and VS1 Clarity. If you move up to an H color, you will pay approximately an extra $1,700 per carat. Move up to F color, the increase will be approximately $1,100 per carat. Improve the color to D and the increase will be approximately $900 per carat.
In other words lets assume a 1 carat diamond of K color = $3000
A 1 carat diamond of D color will be = 3000 +1700+1100+900= $6700
This is more than double the price ( 2.23 times) of K color diamond
Clarity
The clarity of a diamond refers to how clear, or "clean" the diamond is. The more "clean" the diamond, the higher the price. Most diamonds have "imperfections" in them. The clarity scale is a measure of the severity of those imperfections or "inclusions" as it is known in the trade.
For example, a deep break in a diamond which is not that visible when you look at the stone face-up, could sometimes have a greater impact on the clarity of a stone, than a small black crystal which you can see very clearly face-up.
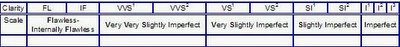
The following is the GIA Diamond clarity-scale:
________________________________________
FL-Flawless
These stones have no imperfections inside or on the outside of the stone under the magnification of a loupe of 10 power.
IF-Internally Flawless
These stones have no inclusions under a loupe with a 10 power magnification.
VVS1,VVS2-Very Very Slightly Imperfect
These stones have very small inclusions which are very difficult to see under a loupe with a 10 power magnification.
VS1,VS2-Very Slightly Imperfect
These stones have small inclusions which are slightly difficult to difficult to see under a loupe with a 10 power magnification.
SI1,SI2-Slightly Imperfect
These stones have inclusions which are fairly easy to see under a loupe with a 10 power magnification, or visible to the naked eye.
I1,I2,I3-Imperfect
These stones have inclusions which range from eye visible to very easily seen to the naked eye.
How much does "clarity" affect cost?
Let's take a typical Diamond for an example, and see what happens when we take it through different clarity grades.
Let's start with a 1.00 carat Diamond of G color and SI1 Clarity. If you move up to a VS1, you will pay approximately an extra $1000 per carat. Move up to VVS1, the increase will be approximately $700 per carat. Improve the clarity to IF and the increase will be approximately $700 per carat.
In other words lets assume a 1 carat diamond of G color and SI1 clarity = $4000
A 1 carat diamond of G color and IF clarity will be = 4000 +1000+700+700= 60 % more
Cut
The cut of a Diamond is the only property which is totally dependent on man. Although often overlooked, cut is actually one of the most important aspects to consider when choosing your diamond. A Diamond cutter analyzes the rough diamond, and has to determine how to extract the most beauty and most profit out of the rough stone.
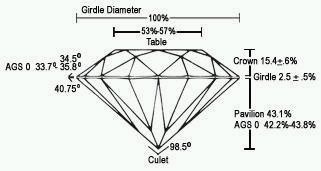
Cut refers to not only the shape of the diamonds, but its proportions and finish, factors which determine the sparkle of the diamond.
It is possible to take the same stone, and depending on which method the cutter decides to use, to either cut it into the most beautiful stone it can be despite heavy weight loss and perhaps lower monetary value. Or else, he can cut a stone to its maximum weight and monetary value, but lose some "brilliance" and "sparkle"!
You see, even if you have two equal polished diamonds, both the same carat size, both the same color, both the same clarity, they may look completely different. How? There are many different shapes, and facets in a diamond. The weight can be distributed in different parts of the stone.
The goal in terms of extracting the greatest beauty from a Diamond, is to have light enter a Diamond, disperse the light as it bounces inside the Diamond, thereby producing the different colors and sparkly effect, and finally returning as much light to the eye as possible.
According to conventional wisdom, the proportions shown at the top of this section are the best for maximum light return.
Cost
The most important "C" you have to think about is COST.
There's no "guideline", since there are too many personal factors to consider. You know your financial situation better than anyone. You have to decide on a budget for how much you want to spend, and/or can afford to spend, and then go out and see what that budget can buy. At the end of the article we will give you ideas on how to save and beat the system.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Find the Diamond Ring of your dreams at great discounts:
Heavenly Treasures
As always we offer a 30 day money back guarantee on every item. Bracelets - Gemstone, Gold, Pearl, Italian Charms, Sterling, Mens, Watches, Diamond, Ankle Earrings, Necklaces, Pins and Pendants - Diamond, Gemstone, Gold, Pearl, Sterling ...
GoldenMine.com
Rings - Wedding, Engagement, Diamond, Platinum, Silver, Gold, Gemstone, Pearl Necklaces - Gold, Silver, Pearl Earrings - Diamond, Gold, Silver, Hoop, Gemstone, Pearl Charms - Gold, Silver, Italian, Diamond, Pearl Diamonds - Loose Diamonds.
Blue Nile
Shop by Product: Diamonds, Engagement Rings, Wedding Rings & Anniversary Rings, Earrings, Necklaces & Pendants, Bracelets, Watches & Accessories Shop by Material: Diamond, Pearl, Gemstone, Platinum, Gold, Silver.
Goldsmiths
... Octavia, Omega, Oris, Philip Stein, Rado, Roberta Coin, Rotary, Seiko, Sirena, Straight from the Heart, Tag Hauer, TechnoMarine, Ted Baker, Tissot, Tommy Hilfiger, Tre Stelle, Trilogy, Union Diamond, Versace, Vertu Phones, White Fire.
Zales, Be Brilliant
Zales Jewelers, the best-known name in retail jewelry, has a broad selection of classic and contemporary styles. In addition to diamond fashion jewelry, Zales offers gold, cultured pearls, and an extensive wedding jewelry selection. ...
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
How much does each "C" affect cost?
Let's take a typical Diamond, and change the various properties to see how it affects the price:
Carat- We saw from the example shown above how much more expensive is 1 carat diamond than 2 diamonds of .5 carats each. It was 3.16 times higher
Color- We also saw how improving on the color from K to D more than doubles the price ( 2.23 times higher)
Clarity -We also saw how improving on the clarity from SI to Fl increases the price by almost 60% .
Cut - Is more complicated. The variables are numerous and therefore should be judged on case by case basis. Usually Belgian cut diamonds are for instance much more expensive than Indian cut diamonds. Part of it is prestige, part of it is supply and demand. India is considered to be the largest diamond cutter in the world in terms of volume.
In order to help our readers get the best value for their money we decided to give you some tips on how to get a nice diamond that you will be proud of without having to rob the bank...
Carat : Most professional couples (according to US statistics) usually settle on ring carats from .7 of a carat to 1 carat.
First tip if you are budgeting to get a diamond of .7 carat, try to settle for .69 instead
You could save per carat about $1100 or $770 per stone
2nd tip color
Once the diamond is mounted on the ring, even an expert cannot tell the exact color category of a diamond. If for instance you move from F to H color you will be able to save about 1100 per carat
This is another saving of $770 per stone of about .70 carat
3rd tip clarity
As in case of color , once the diamond is mounted on the ring, even an expert cannot tell the exact clarity category of a diamond. If for instance you move from VVSI to VSI clarity you will be able to save about $700 per carat or $500 per stone of about .70 carat.
I don't want you to skimp on the cut, because this is by far the most important thing about a diamond.
If you add up the savings per carat= 1100 +1100+700
They add up to $2900 . This is a big chunk of savings for a couple starting their life together.
Now lets say you go to diamond dealer to buy a diamond. You could tell the dealer you want :
.69HVS1 brilliant
If you want to buy a diamond of about 0.70 carat and the dealer will know exactly what you want. If you are not sure about the price of this dealer you can go to another dealer and tell him/her exactly the same code. This allows you to compare one dealer to another based on the same specifications. ( as you can tell this is .69 of carat and not .70. In other words it is 1 point shy of 0.70. This is where the term shy buying came from)
Similarly if you want to buy say a diamond of about one carat you will tell the dealer you want:
.99HVS1 brilliant (similarly this is .99 carat and not 1.00)
It is very important to insist on seeing the diamond you want to purchase in its original sealed pouch. Many dealers offer to issue you their own certificate, this can be misleading since the certificate ( see below) should be issued by an independent gemological lab and not the dealer. GIA and HRD are two of the most respected diamond certifiers in the business.
( The picture on your right shows a typical diamond certificate. Since the certificate is wider and longer we decided only to extract the information that you need most).
A certified diamond has been viewed by an independent gemological lab. The lab has studied the stone carefully and recorded all of its attributes on a certificate. This certificate is a blueprint of the diamond. It lists the shape of the stone, its carat weight and the grades for its color, cut and clarity. The certificate will note any inclusions or blemishes found in the diamond.
So what do you do if you're considering a diamond that is already part of a stunnin platinum setting your fiance has fallen in love with? Ask the jeweler for a store certification. The store should be more than willing to give you a written certificate listing all of the attributes they claim the diamond has. You'll still have to take their word that the diamond is what they say it is, but at least you'll have that word in writing and you will be able to save a lot since once a diamond has already been mounted it loses its certifying premium. This applies to all diamonds that have already been mounted. Again in this case if you want to compare one Jeweler to another you compare based on mounted diamond of equal attributes or specifications.
Some jewelers get upset when customers try to compare based on above, but other jewelers prefer to deal with customers that know what they want. In the end you are going to buy from the jeweler you feel you can trust most.
Since certified diamonds are usually placed in a sealed pouch, the moment the seal is broken and the diamond is removed it should be mounted on the ring. Jewelers will mount the diamond while you are waiting for it.
Finally, to help you speak the jeweler's language, we have added at the end of the article the terms that are commonly used by Jewelers, when they talk about diamonds.
There are hundreds of jewelers in Lebanon, but we elected not to list any, since you can find them everywhere. Our aim is to inform the readers and not to influence their decisions.
We hope this guide will help you in selecting the diamond your fiancé will love and enjoy for life thereafter. The main thing for couples is not to worry if you can't afford the most expensive diamond now, there will be more diamonds in your life. Believe me. I have been there. Good luck,
Diamonds: A Glossary of Terms
Speaking the jeweler's language:
BLEMISH: A flaw on the exterior of a diamond, such as a scratch, abrasion, nick or chip.
BLUE-WHITE: Refers to a diamond that glows (flouresces) blue under ultraviolet light.
BRILLIANCE: White light reflected back from a diamond.
BRILLIANT: A round diamond with 58 facets.
CARAT: A unit of weight, equal to 200 milligrams. In ancient times one carat was equal to one carob bean or four grains of rice.
CARBON: The raw material of which diamonds are made. Occasionally a diamond will contain tiny pockets of carbon which can be seen as black spots within the stone.
CLOUD: A cluster of small inclusions, or internal flaws, within a diamond.
CROWN: The top of a diamond. Everything above the girdle.
CULET: The bottom facet of a diamond, usually very small.
DISPERSION: Colored light reflected from within a diamond; also called fire.
EYE-CLEAN: Refers to a diamond that has no inclusions or blemishes visible to the naked eye.
FACET: A polished surface on a diamond. A round, full-cut diamond usually has 58 facets.
FLUORESCENCE: A diamond's reaction to ultraviolet (UV) light, causing the stone to glow in various colors.
FULL-CUT: A diamond with 58 or more facets.
GEMOLOGIST: A person who has been trained and accredited in diamonds and colored stones.
GIA: Gemological Institute of America, an independent, non-profit organization which sets and upholds standards for grading diamonds and other precious stones.
GIRDLE: The narrow, unpolished band around the widest part of the diamond; the girdle separates the crown and the pavilion of the stone.
HEAD: The prongs which hold a diamond in its setting.
INCLUSION: A flaw within a diamond, such as carbon spots or fractures.
KARAT: The measure of the purity of gold; 24-karat being pure gold. Jewelry is made from 18K and 14K gold, which contain other metals for strength.
LASER-DRILLED: A diamond that has been treated with a laser to remove carbon spots.
LOUPE: A small magnifying glass used to view gemstones
OFF-MAKE: A poorly proportioned diamond.
PAVE: A method of setting diamonds very closely together, giving the illusion of one or more larger diamonds.
PAVILION: The bottom of a diamond; everything below the diamond's girdle.
POINT: One-hundredth of a carat. A diamond weighing one-and-a-half carats weighs 150 points.
SEMI-MOUNT: A setting which is complete except for the main stone, which will be selected separately.
SINGLE-CUT: A diamond with only 16 or 17 facets.
SPARKLE: The liveliness of the light reflecting from a diamond; the sum of the brilliance and the fire (dispersion).
TIFFANY: A simple, elegant 2-3mm ring setting with a head that holds a single diamond.
COMMENTS: SAY SOMETHING!
Home
Subscribe to The Diva Network


            
|